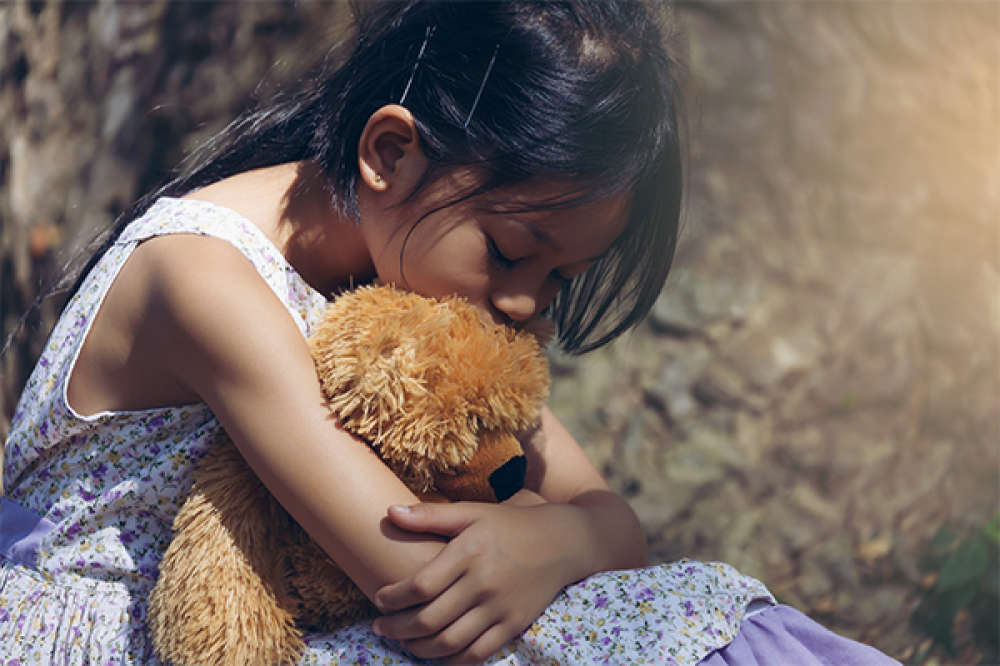
Childhood Anxiety Disorder
The anxiety is normal for all children to feel sad or anxious from time to time. They may experience anxiety when they are entering schools to a new area or situation. The child starts experiencing a stressful event. It affects their behaviour and thought pattern in day to day living such as school, home and social life. They are more worried about school performance, relationship and health. Latterly it becomes a serious issue in every child in life. A child must be assessed and treated with Neuro-Psychiatrist and trained therapist.
Prevalence
In India, 25.1% of the 13 to 18 age groups of children facing anxiety disorder are school-going children. Both male and female children are equally affected by an anxiety disorder. The 5.9% 13 to 18yrs age group children have a severe anxiety disorder
Signs and Symptoms
If a child experiences the following anxiety symptoms, the parents or primary caregiver should take him/her to a treatment centre. The symptoms are
- -Difficulty in concentration
- -Getting easily irritable and anger outburst
- -crying
- -Not eating properly
- -Not sleeping properly
- -While sleeping experiencing bad dreams
- -Consistently worrying and negative thoughts
- -Frequently reporting muscle pains all over the body
- -Digestive problem
- -Using toilets often
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Types of Childhood Anxiety Disorder
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Children with disorder highly worry about past, present and future events. They keep on worrying about past discussions and events. They fear future tasks and upcoming life events such as school academics, family relationships with peers, sports, and health conditions. They may also get always reassurance from others.
Panic Disorder
Panic disorder is diagnosed if children suffer from sudden and two or more recurrent unexpected anxiety attacks without any reason in the last one month. The children begin to avoid and fear going outside, playing, interacting or engaging in any single or group activities, and fearful thoughts.
Separation Anxiety Disorder
This disorder is most common for seven to nine years of children. If the parent leaves their children first time in school or leaves in a home and siblings or other family members, the child gets fear about that separation. Laterally the child accommodates that new situation. The few old children were not able to accept separation from parents or caregivers. So they may experience anxiety symptoms, refusing to go to school or hostel homesickness
- Specific Phobias
Children may experience persistent excessive and unreasonable fears of an object or a situation. They are unable to control that fear and may not realize it is unreasonable. (E.g. dogs, injection, dark night, spiders, anxiety about height flying etc.) So children avoid or distress particular things in daily life, school functioning, family functioning, or social relationships. They may express their anxiety by crying, tantrums, increased heart rate, sweaty palms etc.
Selective Mutism
Selective Mutism is one of the most commonly social anxiety disorders that children suffer from. Those children are unable to speak and communicate in select social situations effectively. Therefore, they remain calm in that situation, do not maintain eye contact with others or avoid that particular action or event.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
Obsessive-Compulsive disorder is a childhood anxiety disorder. It causes repeated thoughts (obsessions) and feeling, compelled to perform those activities repeatedly (compulsions). After those compulsions, they can feel a bit more relaxed. Children mostly get diagnosed at the age of ten. Boys are more likely to develop OCD. Girls may develop it during adolescence. The causes of OCD in children are expecting more perfection and cleanliness from parents and schools.
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Children with posttraumatic stress disorder could have extreme fear and anxiety about past experienced life-threatening traumatic events or victim by others. The causes of PTSD are; unexpected parent death, domestic violence, physical or sexual abuse, natural or human-made disasters (such as fires, hurricanes, or floods). After such events, children cannot recover from these feelings, emotionally numb and lead to a mental health problem.
Treatment
In treatment, psychotherapy and pharmacology play a vital role in childhood anxiety disorders.
Psychotherapy
Cognitive behaviour therapy
Cognitive therapy is an effective therapy to treat childhood anxiety disorders. CBT skills and techniques are very helpful for children to overcome anxiety disorders.
Parental Psychoeducation
The parent has to be educated about the nature of illness what their child is suffering to get maximum support from family members and act as co-therapist.
Relaxation and Breathing Techniques.
Several relaxation techniques are being used to overcome anxiety. Breathing plays an important role. By modifying breathing patterns, we can rejuvenate the brain cells, making the client calm, and compose.
Cognitive restructuring
The transactional analysis, rational emotive behaviour techniques are helpful to overcome negative thoughts, feelings, etc.
Guided Imaginary
This is one relaxation technique, which makes the clients relax by using five sensory organs. This is more effective in anxiety disorder
Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP)
ERP is a very useful therapy for children with OCD. It’s often used along with medications. Exposure refers to the gradual and repetitive exposure of an individual to their feared situations ideas (for example, someone with contamination obsessions thinking about the fear of any disease.