Obesity
Obesity is excess body fat; fat at undesired parts of the body, disfiguring one and hindering daily life
Overweight is excess body weight than needed for the age and height
Morbid obesity: obesity with comorbid conditions
Obesity is measured by Body mass index (BMI)
Weight (kg) ÷ (height in meters)2
- overweight is a BMI greater than or equal to 25
- obesity is a BMI greater than or equal to 30.

WHO key facts March 2020
- Worldwide obesity has nearly tripled since 1975.
- In 2016, more than 1.9 billion adults, 18 years and older, were overweight. Of these, over 650 million were obese.
- 39% of adults aged 18 years and over were overweight in 2016, and 13% were obese.
- 40 million children under the age of 5 were overweight or obese in 2018.
- Over 340 million children and adolescents aged 5-19 were overweight or obese in 2016. Most of the world’s population live in countries where overweight and obesity kills more people than underweight.
- Obesity is preventable.
This is an alarming trend because childhood obesity carries to adolescents and adulthood
This significantly contributes to the early onset of non-communicable diseases like Diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases.
Obesity precipitates depression during their entire lifetime.
Causes of obesity
The most important cause of obesity is the mismatch between diet and exercise.
Genetics: Leptin deficiency (LEP), Leptin receptor deficiency (LEPR), increase appetite, reduces satiety.
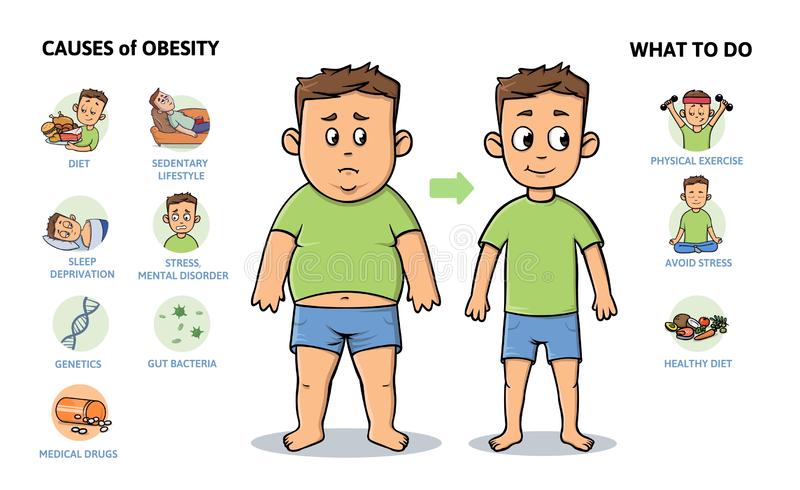
Environmental factors: increased sedentary lifestyle, lack of playgrounds, sidewalks, preferring to use a motor vehicle for short-distance travel, both parents and school encourage academics than sports.
Media influence and television ads
Diet: high fat, high-calorie diet, the child prefers to aerated sugary beverages than plain water, eat during boredom, eat while watching movies or playing with mobile. Eat-in between meals
Endocrine disorders – hypothyroidism, cortisol excess, Growth hormone deficiency
Effects of obesity
Physical effects
- Breathlessness increased sweating, snoring, fatigue, multiple joint pain
- Increased incidence of type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnoea, osteoarthritis, and thus cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases
Psychological effects
- Obesity negatively affects self-esteem
- Depression and anxiety are common among obese than age-matched normal-weight persons.
The above two leads the individual to adhere poorly to the diet and exercise programmes
Thus the quality of life in obese individuals has deteriorated in proportion with the level of obesity.
Management of obesity:
Management of obesity can include lifestyle changes, medications, or surgery.
The main treatment for obesity consists of weight loss via dieting and physical exercise.
Diet programs can produce weight loss over the short term and long-term, although combining exercise and counselling provides greater results.
Medications aimed at reducing appetite (topiramate 25-100mg), increasing fat metabolism (Beta-methyl-phenylethylamine (Fastin), reducing fat absorption (Orlistat).
These medications have equal side effects as effects
Surgery: popularly known as Bariatric surgery to reduce the stomach’s size, linking gut with the intestine.
Diet: prefer
-Whole grains (whole wheat, brown rice, maize, ragi, other millets )
-Vegetables (green leafy, those in creepers, roots, then tubers )
-Whole fruits (not fruit juices)
-Nuts, seeds, beans, and other healthful sources of protein (fish and poultry)
-Plant oils (olive and other vegetable oils)
Exercise:
Activity for a lesser period only maintains the weight, and it is found that 30-60 min of exercise helps to burn the excess fat.
Brisk walking is proffered over jogging or other workouts
Yoga helps in both maintaining physical and psychological well being
Conclusion:
Obesity is a psychiatric disorder with both physical and psychological symptoms and long term complications
Prevention to be aimed at the school level.